Discover the Alhambra: A Palace, Fortress, and City Frozen in Time
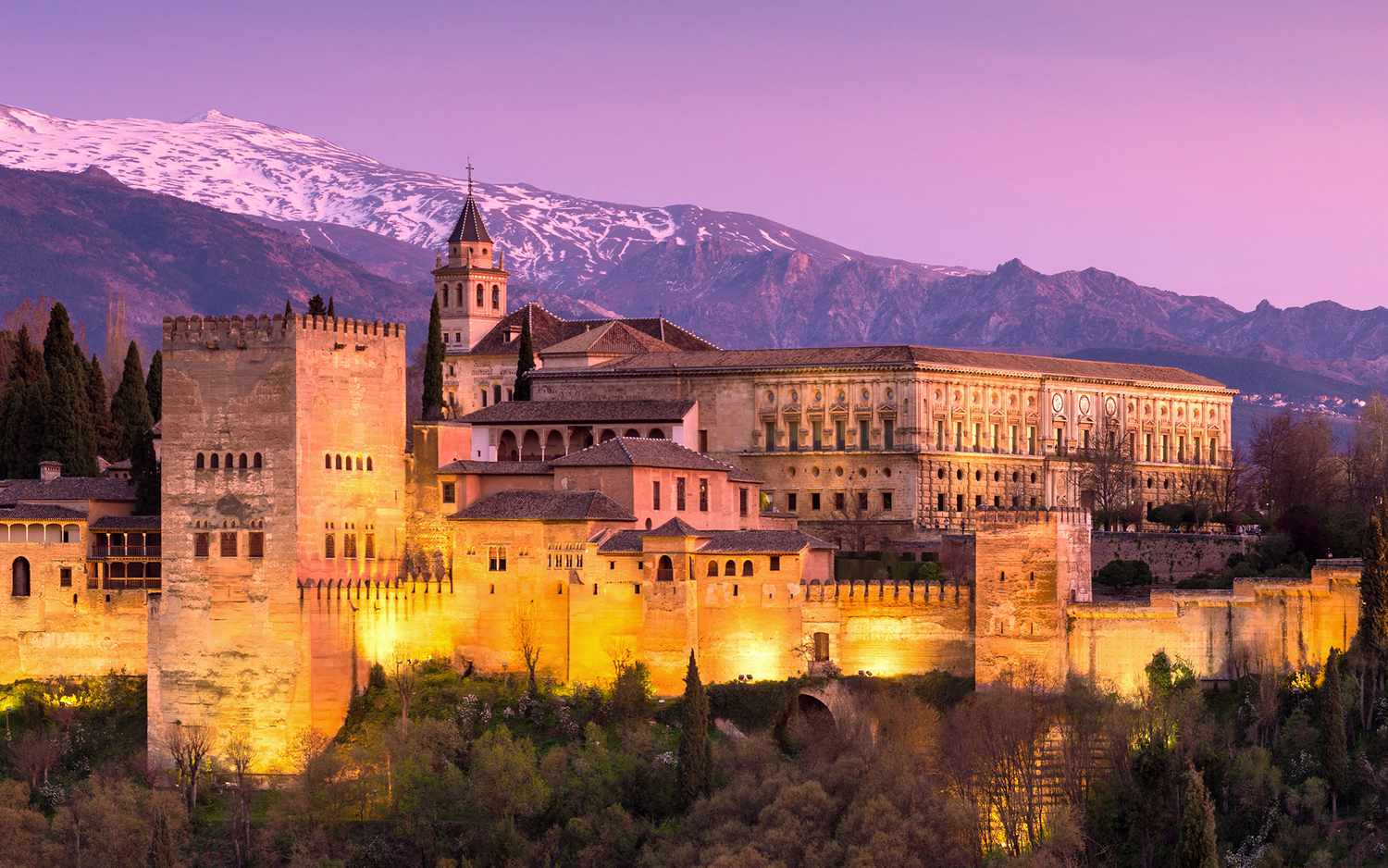

The Alhambra, located in Granada, Spain, is a palace and fortress complex that showcases the rich history and architecture of Islamic civilization. This article will explore the history of the Alhambra, its architectural features, and its significance in modern times.
The Alhambra
The Alhambra's history is a rich tapestry of Moorish and Islamic influences, with its construction dating back to the 9th century.
The original fortress was built by the Moors, who were Muslims from North Africa, and was later modified by successive rulers, including the Nasrid dynasty, who transformed it into a royal palace in the 13th century.
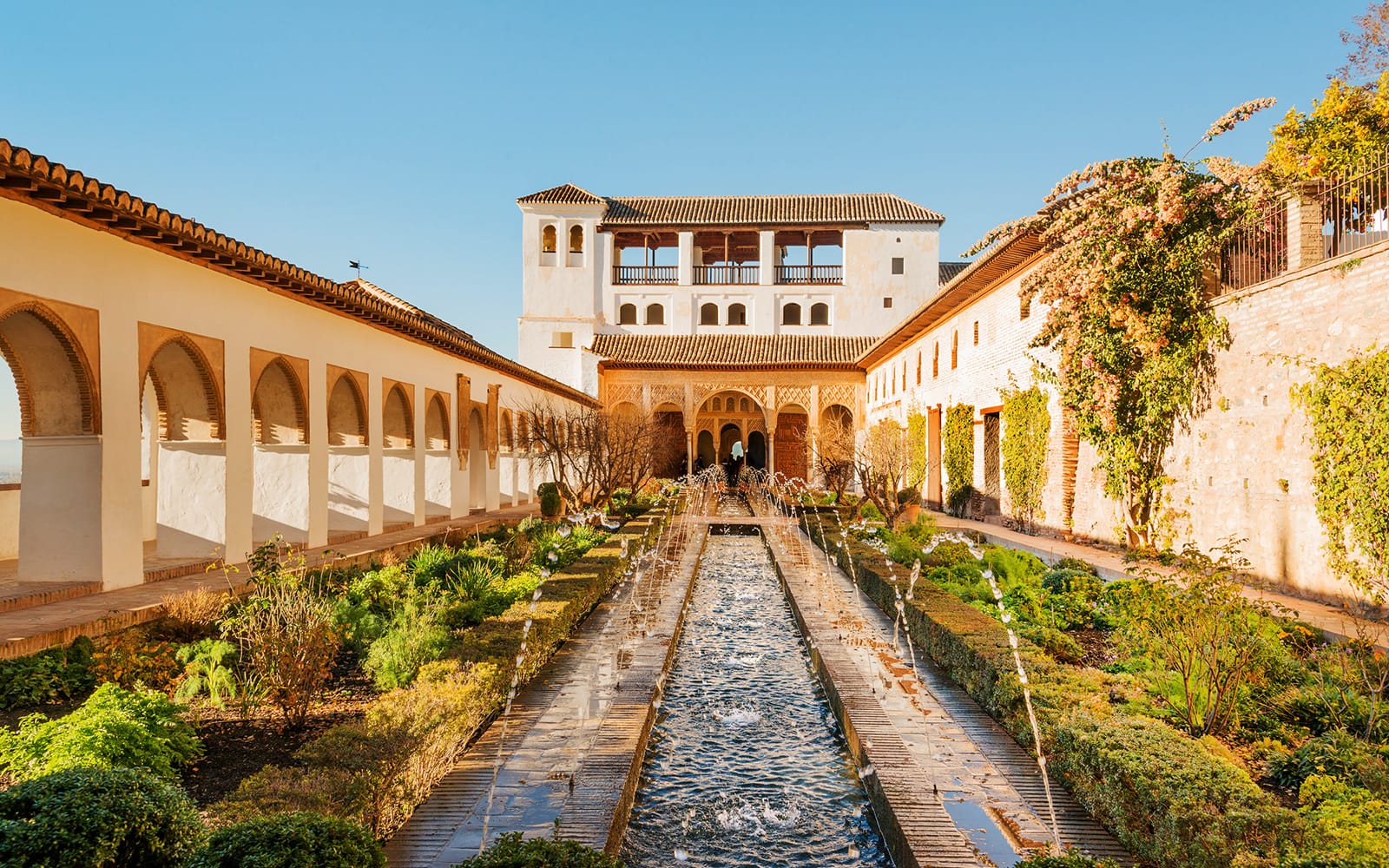

The Alhambra's architecture is a testament to the cultural exchange between the Islamic world and Europe during the Middle Ages. The site's intricate stone carvings, ornate tile work, and serene courtyards reflect the Moorish emphasis on beauty and tranquility.
As a symbol of Islamic architecture, the Alhambra has had a profound influence on the development of architecture in Spain and beyond.
Its unique blend of Moorish, Gothic, and Renaissance styles has inspired countless imitations and adaptations, cementing its status as a cultural icon.
The Palaces and Architecture
The Alhambra is home to several palaces, each with its unique architectural features and historical significance. The Mexuar, also known as the Council Room, is a relatively plain palace that served as a reception area for dignitaries.
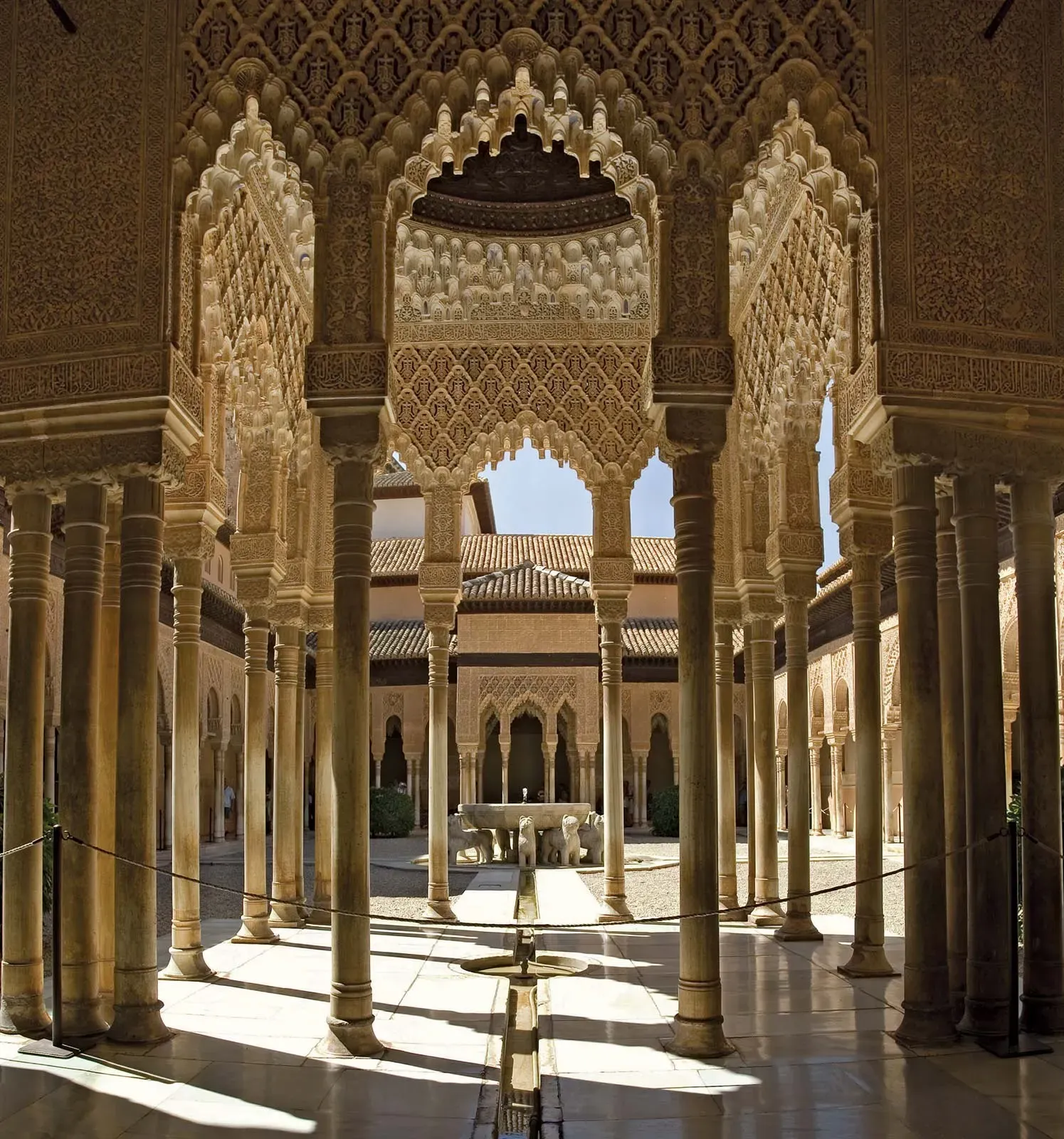

In contrast, the Comares Palace, built during the reign of Yusuf I, is a masterpiece of Moorish architecture, with its intricate decorative motifs and serene courtyards. The Palace of the Lions, another iconic palace, boasts an impressive courtyard surrounded by 124 slender columns and a stunning fountain.
The Partal Palace, a less-known but equally impressive palace, features a beautiful reflecting pool and ornate arches. Moorish architecture is characterized by the use of courtyards, water features, and decorative motifs, which are evident in these palaces.
The use of arches, domes, and columns creates a sense of harmony and balance, while intricate geometric patterns and calligraphy adorn the walls and ceilings. The palaces within the Alhambra are a testament to the ingenuity and craftsmanship of Moorish architects, who successfully blended functionality with aesthetics to create a truly unique and breathtaking architectural style.
Restoration and Modern Significance
Restoration and Modern Significance The Alhambra's rediscovery in the 19th century marked the beginning of a new era for the ancient palace and fortress. As interest in Moorish architecture and Spanish history grew, so did the need for restoration and preservation.
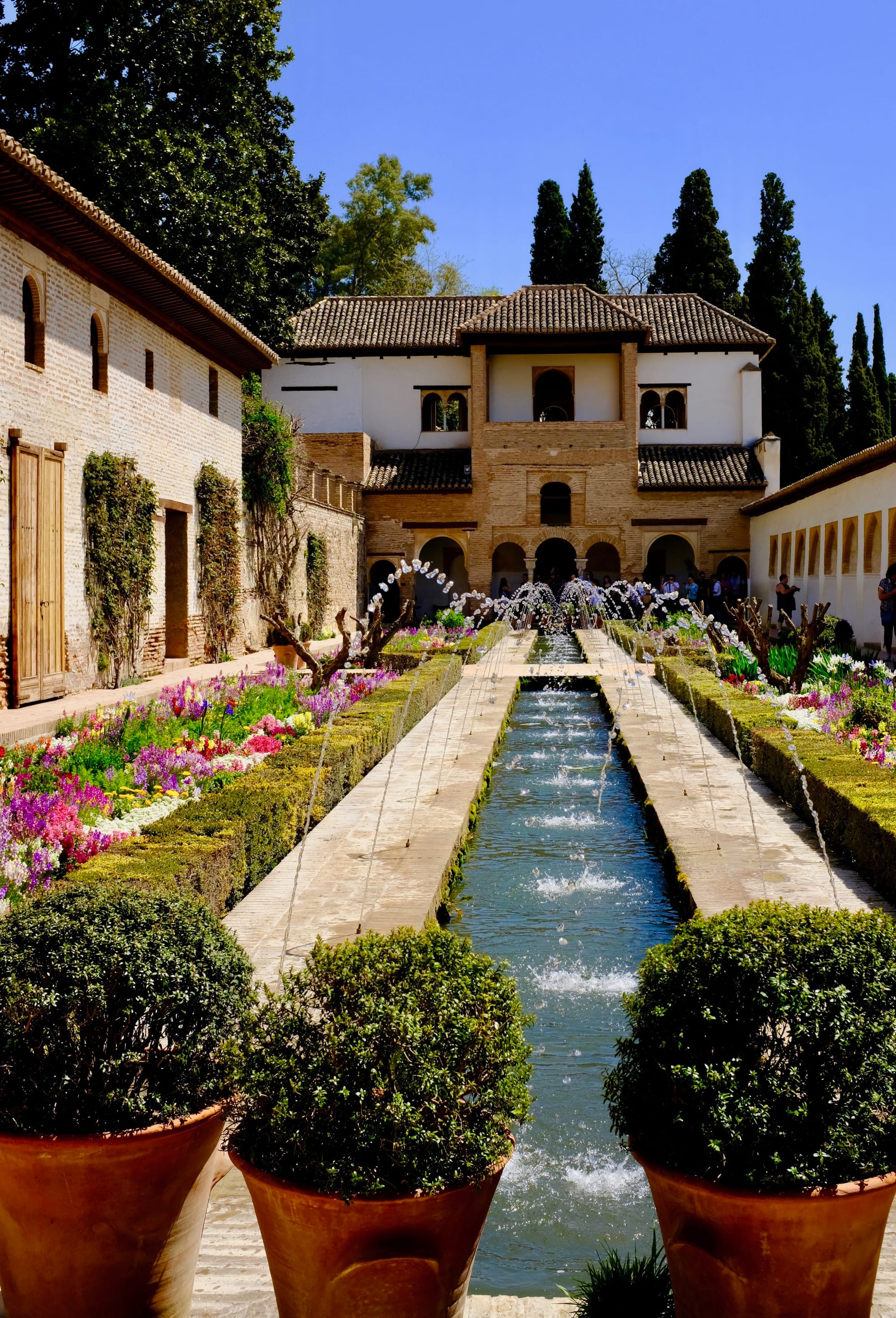

In 1870, the Spanish government declared the Alhambra a national monument, and a series of restoration projects were undertaken to repair the damage caused by centuries of neglect. The most notable restoration was led by architect Leopoldo Torres Balbás, who worked tirelessly to restore the complex to its original glory.
Today, the Alhambra is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and one of Spain's most beloved tourist attractions, drawing millions of visitors each year. Despite the challenges of preserving a site of such historical significance, the Alhambra remains a testament to the ingenuity and craftsmanship of the Moors, and a source of pride for the people of Granada.
Conclusions
In conclusion, the Alhambra is a unique and fascinating historical site that offers a glimpse into the rich cultural heritage of Islamic Spain. Its stunning architecture, intricate decorations, and complex history make it a must-visit destination for anyone interested in history, architecture, or culture