Glutathione Benefits: The Ultimate Guide to this Powerful Antioxidant

Glutathione is a powerful antioxidant found in every cell. Glutathione is naturally produced by the human body and is available in some foods. Glutathione levels naturally decrease with age. However, factors like poor diet and a sedentary lifestyle can also reduce glutathione levels. Increasing glutathione may provide numerous health benefits, including reducing oxidative stress and potentially slowing cancer progression.
What is Glutathione?

Glutathione is made up of three amino acids: glutamine, glycine, and cysteine. Glutathione acts as an important antioxidant. This means it helps combat free radicals, molecules that can damage the body’s cells. Glutathione plays a role in many chemical reactions in your body.
It also helps detoxify chemicals, including some that your body creates naturally, as well as pollutants and drugs.
What are the Benefits of Glutathione?

Glutathione has many vital roles in supporting overall health, including neutralizing free radicals and regenerating vitamins C and E. Glutathione may:
- Reduce inflammation and oxidative damage
- Promote cardiovascular health
- Slow cancer progression
- Slow aging processes
- Improve immune function
- Prevent neurodegenerative conditions
- Minimize cell damage from liver disease
- Improve insulin resistance
How to Increase Glutathione Levels Naturally

People can naturally increase their glutathione levels by making dietary and lifestyle-related changes.
- Eat Sulfur-Rich Foods: Eating sulfur-rich foods, such as meat, fish, poultry, and cruciferous vegetables like broccoli, may increase glutathione levels.
- Consume Dairy Products: Dairy products contain the protein beta-casein, which has the potential to increase glutathione levels, especially dairy milk containing only the A2 beta-casein protein.
- Consume Whey Protein: Whey protein is another protein that comes from dairy and contains large amounts of cysteine, an important amino acid involved in glutathione synthesis.
- Get Regular Exercise: Regular exercise may reduce oxidative stress by increasing glutathione levels.
- Get Enough Sleep: Long-term lack of sleep may decrease glutathione levels, so make sure you get good, restorative sleep each night.
- Limit Alcohol Intake: Excessive alcohol use is linked to a depletion of glutathione levels, especially in the lungs, so limiting alcohol consumption may help maintain healthy glutathione levels.

Glutathione Supplements
In addition to naturally increasing glutathione levels, it’s also available as an oral supplement, and can be given intravenously, topically, or as an inhalant.
Research suggests that a glutathione-rich diet may not produce clinically significant results due to glutathione’s low bioavailability, meaning the human body has a hard time using it.
However, several supplements may boost the body’s production of glutathione, such as:
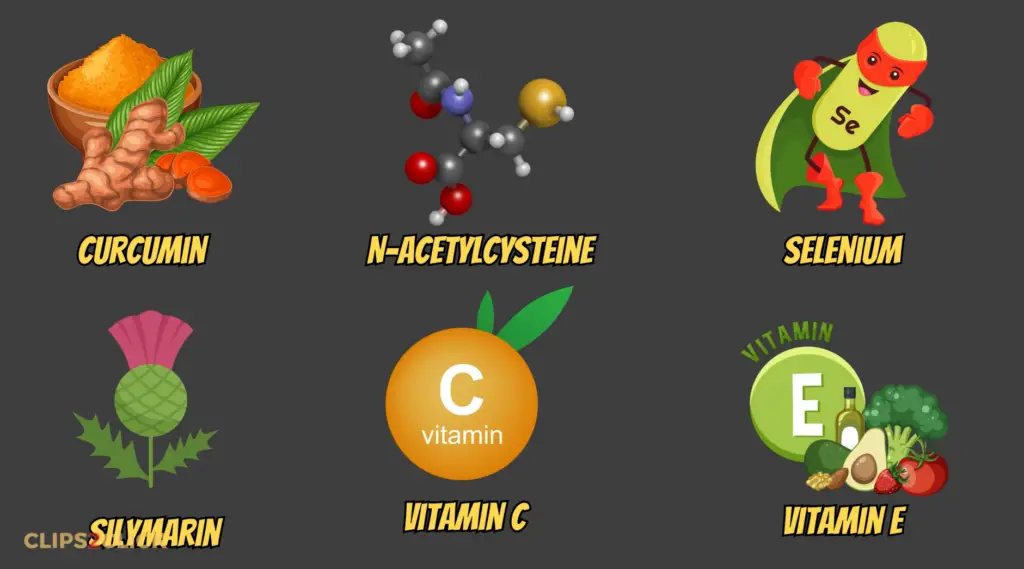
- Curcumin
- N-acetylcysteine
- Selenium
- Silymarin
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin E
- Milk thistle
- Whey protein
Glutathione Side Effects
There is limited information regarding the side effects of glutathione. The FDA has warned against using glutathione powder from certain distributors due to potential contamination with high quantities of endotoxins.
Endotoxins can cause adverse effects such as nausea, vomiting, lightheadedness, body aches, chills, low blood pressure, and difficulty breathing.
Things to Consider

- Researchers have questioned the effectiveness of glutathione supplementation due to its low bioavailability.
- The human digestive system quickly breaks down water-soluble compounds such as glutathione, so eating glutathione-rich foods or taking oral glutathione supplements may not produce clinically significant results.
- Talk to your doctor before starting glutathione supplementation to determine whether it will be safe or effective.
- Dietary supplements are not regulated in the same way as drugs are in the United States. Therefore, it’s important to talk to your healthcare provider about any supplements you plan to take.
Products
The Bottom Line
Glutathione is an important antioxidant that supports various aspects of human health. Preliminary studies suggest that low glutathione levels may contribute to different disease states.
However, its exact roles in disease development and prevention remain unclear. While glutathione supplements may be appropriate for some people, they may not be safe for everyone and could interact with other medications a person is taking.
References
- Berkheiser, K. (2018). 10 Natural Ways to Increase Your Glutathione Levels. [online] Healthline. Available at: https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/how-to-increase-glutathione.
- www.medicalnewstoday.com. (2019). How to increase glutathione levels: 4 natural ways. [online] Available at: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/326196.
- Metcalf, E. (2013). Glutathione. [online] WebMD. Available at: https://www.webmd.com/vitamins-and-supplements/glutathione-uses-risks.
- Healthline. (2017). Phosphatidylcholine: Benefits, Side Effects, and More. [online] Available at: https://www.healthline.com/health/food-nutrition/phosphatidylcholine.
- Wong, C. (2022). What Is Glutathione and What Are the Benefits? [online] Verywell Health. Available at: https://www.verywellhealth.com/benefits-of-glutathione-89457.
- WebMD (2019). Glutathione: Uses, Side Effects, Interactions, Dosage, and Warning. [online] Webmd.com. Available at: https://www.webmd.com/vitamins/ai/ingredientmono-717/glutathione.