Rome's Colosseum: History of Engineering Marvel of Ancient Roman
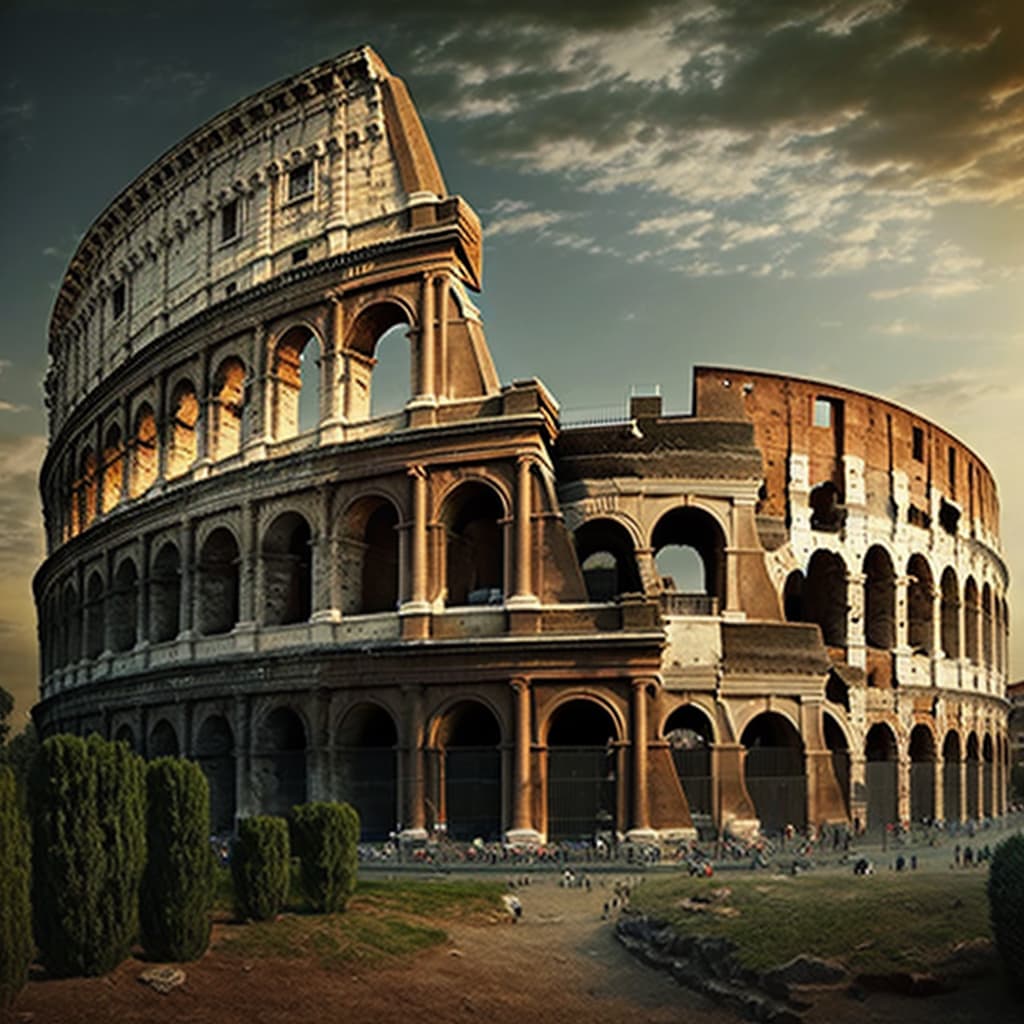

The Colosseum is one of the most iconic landmarks in Rome, Italy, and a testament to the engineering and architectural skills of the ancient Romans. As the largest ancient amphitheatre ever built, it is a remarkable feat of construction that has withstood the test of time.
In this article, we will explore the history of the Colosseum, its design and events, and its legacy in modern times.
History of the Colosseum
The history behind the Colosseum's construction is a complex one, spanning several decades and involving the reign of three emperors. Construction began under the Emperor Vespasian in 72 AD and was completed in 80 AD under his successor, Titus.
Further modifications were made during the reign of Domitian. The Colosseum was built as a symbol of power and engineering in ancient Rome, showcasing the city's wealth and grandeur. It was the largest amphitheatre ever built, with a capacity to hold up to 80,000 spectators.
The building's design and construction were influenced by the Flavian dynasty, who were known for their architectural achievements. The Colosseum's significance in ancient Rome was not only as a venue for entertainment but also as a symbol of the empire's power and engineering prowess.
Design and Events of the Colosseum
The Colosseum's design was a major factor in its success as a venue for various events. Its elliptical shape and large size allowed it to hold a massive audience of up to 80,000 spectators, who could gather to watch gladiatorial contests, animal hunts, executions, and other public spectacles.
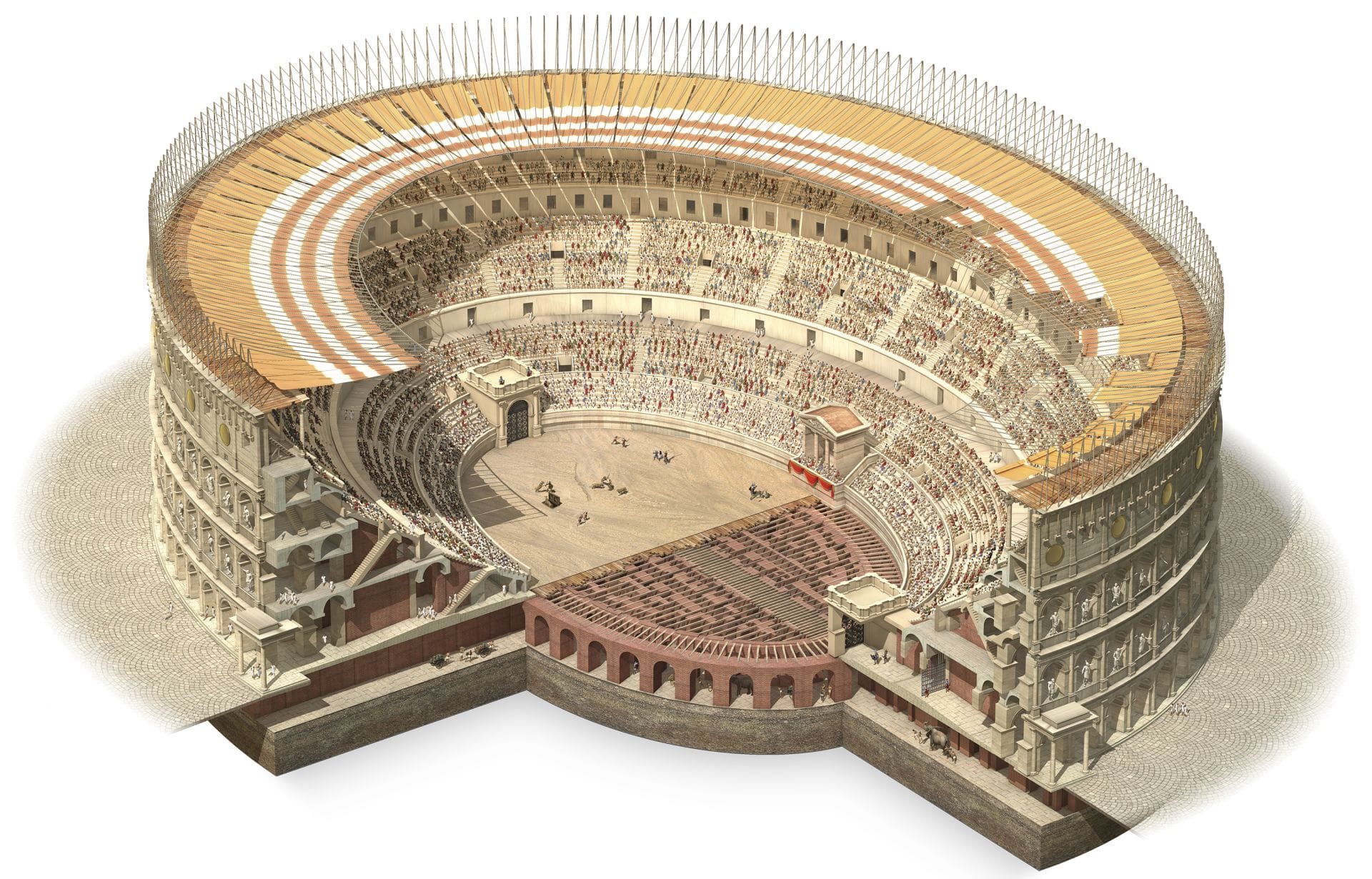
The building's design also incorporated a complex system of pulleys, counterweights, and ramps that enabled the quick setup and removal of scenery for different events. This allowed for a wide range of events to be held at the Colosseum, from gladiatorial contests to dramas based on Roman mythology.
The Colosseum's design also included a network of underground tunnels and chambers that provided space for gladiators, animals, and scenery to be stored and prepared for events. Overall, the Colosseum's design was a key factor in its success as a venue for entertainment and spectacle in ancient Rome.
Legacy of the Colosseum

The Colosseum's legacy extends far beyond its ancient past, as it remains a renowned symbol of Imperial Rome and a testament to the city's rich history.
Despite being substantially ruined by earthquakes and stone robbers, the Colosseum continues to captivate audiences worldwide, attracting millions of tourists each year. Its significance in modern times is multifaceted, serving as a cultural icon, a historical landmark, and a source of inspiration for artists, architects, and engineers.
The Colosseum's enduring presence has also led to its inclusion as one of the New 7 Wonders of the World, solidifying its status as an irreplaceable part of human heritage.
Furthermore, the Colosseum's connection to the Catholic Church is evident in the annual torchlit "Way of the Cross" procession led by the Pope on Good Friday, which begins in the area surrounding the ancient amphitheatre.
Conclusions
The Colosseum is a true marvel of ancient Roman engineering and a testament to the power and grandeur of the Roman Empire.
Its rich history, stunning architecture, and continued significance in modern times make it a must-visit destination for anyone interested in history, architecture, or engineering. As one of the New 7 Wonders of the World, the Colosseum continues to inspire awe and wonder in people around the world.