Salivary Gland Cancer: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
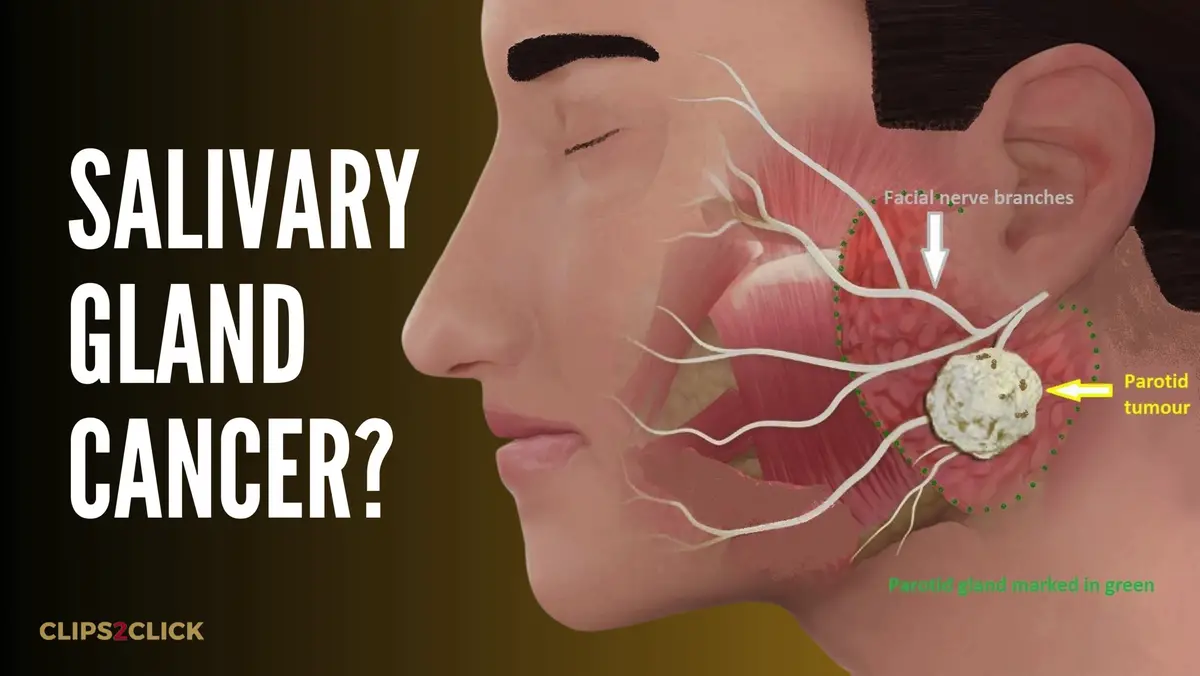
Salivary gland cancer is a rare type of cancer that forms in the salivary glands. Salivary glands produce saliva, which helps with digestion. There are several different salivary glands in and near your mouth. Most salivary gland tumors are benign, but malignant tumors can also develop.
Salivary gland cancers are uncommon malignancies and represent less than 5% of head and neck cancers. This blog post will discuss salivary gland cancer symptoms, causes, and treatment.
Types of Salivary Glands
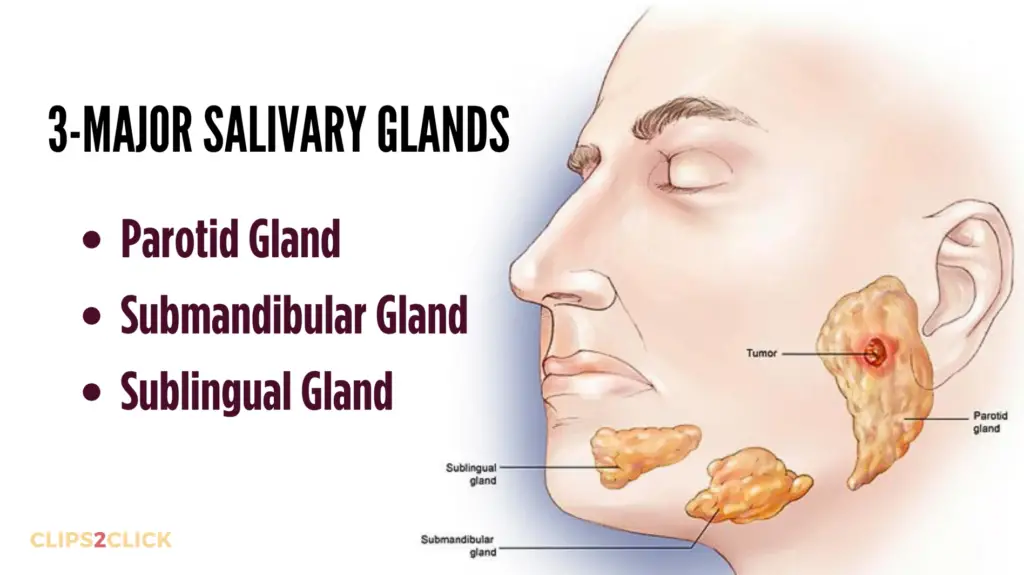
There are three major salivary glands on each side of the face:
- Parotid glands: Located inside each cheek.
- Submandibular glands: Located below the jawbone.
- Sublingual glands: Located along the floor of the mouth.
Hundreds of microscopic minor salivary glands are too small to see without special equipment. Tumors are uncommon in these glands but are more often malignant. The parotid gland is the most common location for both benign and malignant tumors.
Types of Salivary Gland Cancers

There are many types of salivary gland cancers. They are named according to which cell types they most resemble. The most common types are mucoepidermoid carcinoma and adenoid cystic carcinoma which together make up half of all malignant salivary gland tumors.
Salivary gland cancers can metastasize to other body parts through the bloodstream or lymphatic system. The lungs, bone, and liver are common sites of metastasis.
What Causes Salivary Gland Cancer?

The exact cause of most salivary gland cancers is unknown. However, several risk factors can increase your chances of developing this disease.
- Radiation exposure: Previous radiation therapy to the head and neck increases the risk of developing salivary gland cancer.
- Workplace exposures: Exposure to certain substances in the workplace, such as nickel, rubber, and silica, may increase your risk.
- Age: Salivary gland cancer is more common in older adults.
- Genetics: Having a family history of salivary gland cancer may increase your risk.
- Smoking and alcohol use has been linked to an increased risk of salivary gland cancer.
What are the First Symptoms of Salivary Gland Cancer?
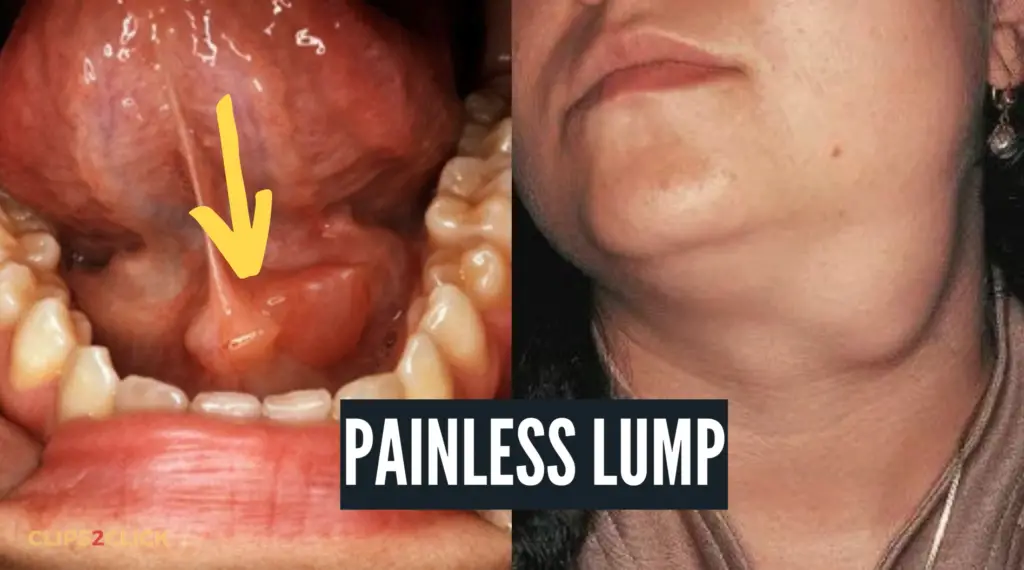
Salivary gland cancer symptoms vary depending on the tumor’s location and size. However, the most common salivary gland cancer first symptom is a painless lump or swelling in the: Face, Neck, Jaw, Mouth.
Other symptoms may include:
- Numbness or weakness in the face
- Persistent pain in the face, jaw, neck, or mouth.
- Difficulty opening the mouth fully.
- Trouble swallowing.
- Bleeding from the mouth.
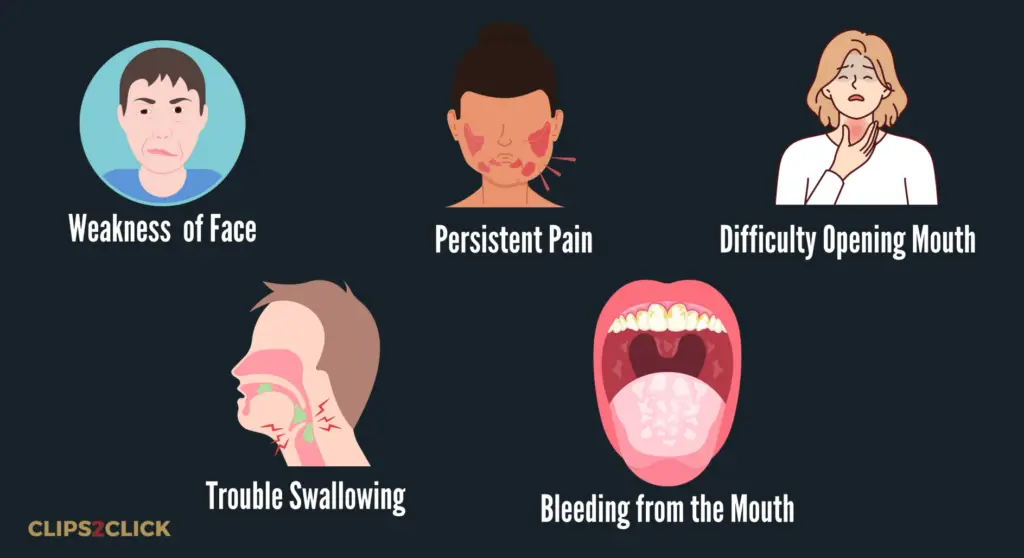
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to see your doctor as soon as possible.
How is Salivary Gland Cancer Diagnosed?
Diagnosing salivary gland cancer involves a physical exam, review of your medical history, and tests. Your doctor will:
- Check for lumps or swelling in the salivary glands.
- Test how your facial nerves are responding.
- Ask about your symptoms.
Your doctor may recommend imaging tests such as:
- CT scan: A CT scan uses X-rays to create images of the inside of your body and can show the size and location of a parotid gland tumor.
- MRI: An MRI uses magnets and radio waves to create images of the inside of your body and can help determine if the cancer has spread to soft tissue.
- PET scan: A PET scan can show if the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes or other body parts.
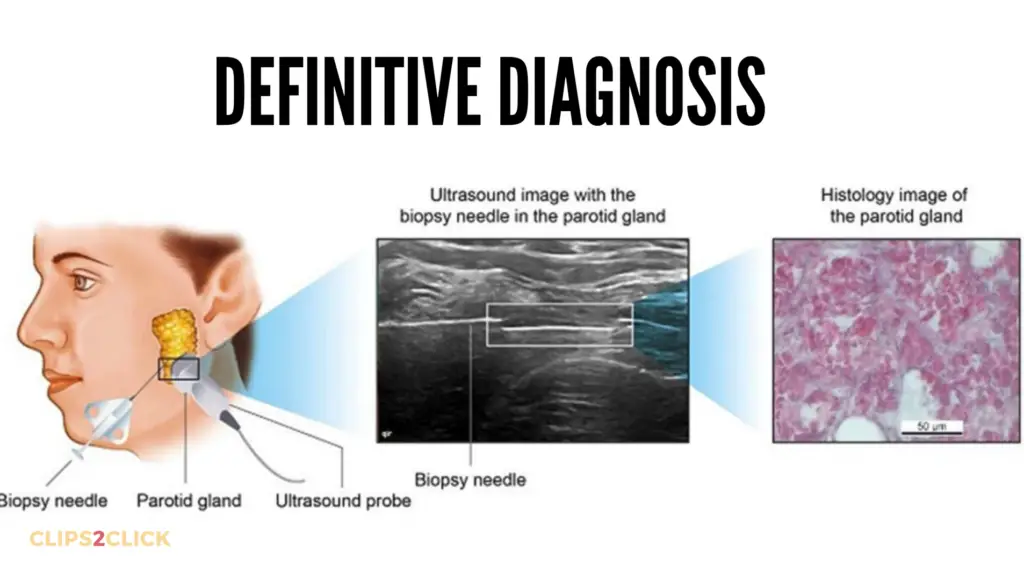
The only way to confirm a salivary gland cancer diagnosis is with a biopsy. A biopsy involves removing a small sample of tissue from the tumor and examining it under a microscope.
Salivary Gland Cancer Prognosis

The salivary gland cancer prognosis varies depending on several factors, including:
- The stage of the cancer: The stage of cancer describes the size of the tumor and how far it has spread.
- The tumor’s location: Tumors located in certain salivary glands may be more aggressive.
- Your age and overall health: Older adults and those with other medical conditions may have a worse prognosis.
- The grade of the tumor:
- The presence or absence of lymph node involvement
Salivary Gland Cancer Treatment
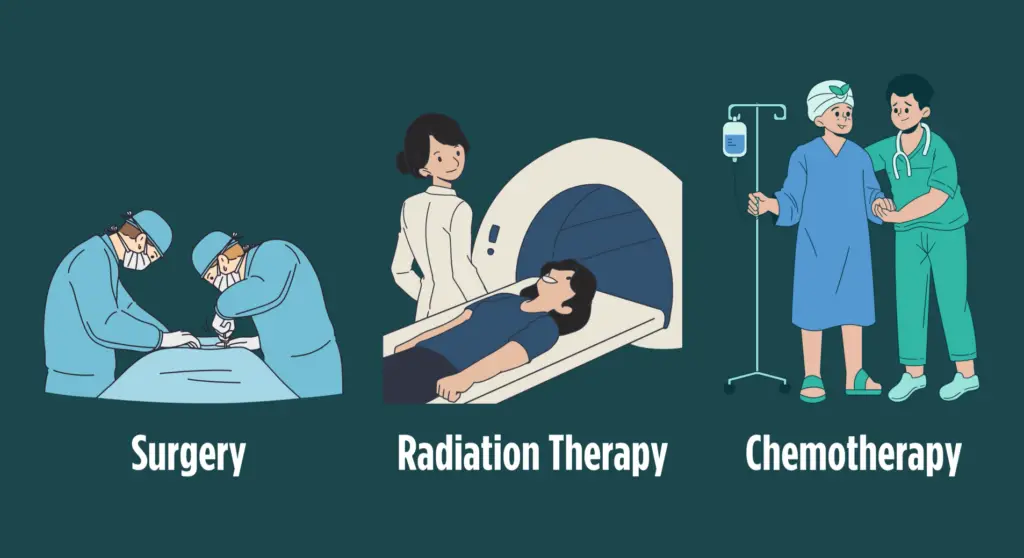
Treatment for salivary gland cancer depends on several factors, including the cancer stage, location, and your overall health. The most common treatment is surgery to remove the tumor. Other treatment options may include:
- Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells. It’s often used after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells. It may be used before or after surgery to shrink the tumor or kill any remaining cancer cells.
- Targeted therapy uses drugs to target specific proteins or genes that help cancer cells grow.
Living as a Salivary Gland Cancer Survivor
Living with salivary gland cancer can be challenging. However, there are things you can do to cope with the disease and its treatment.
- Join a support group
- Talk to a therapist or counselor
- Eat a healthy diet
- Exercise regularly
- Get enough sleep
If you have been diagnosed with salivary gland cancer, it is important to talk to your doctor about your treatment options and what you can expect.
Disclaimer: The information in this blog post is for informational purposes only and should not be construed as medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment.