Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms and How to Overcome Them
Vitamin D deficiency is a widespread issue that affects millions of people worldwide. Often referred to as the “sunshine vitamin,” vitamin D plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being.
However, many individuals overlook the subtle signs of deficiency, leading to a host of potential health problems. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the common vitamin D deficiency symptoms, risk factors, and effective treatment strategies to help you regain optimal vitamin D levels.
Common Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency:
1. Frequent Illnesses and Infections:
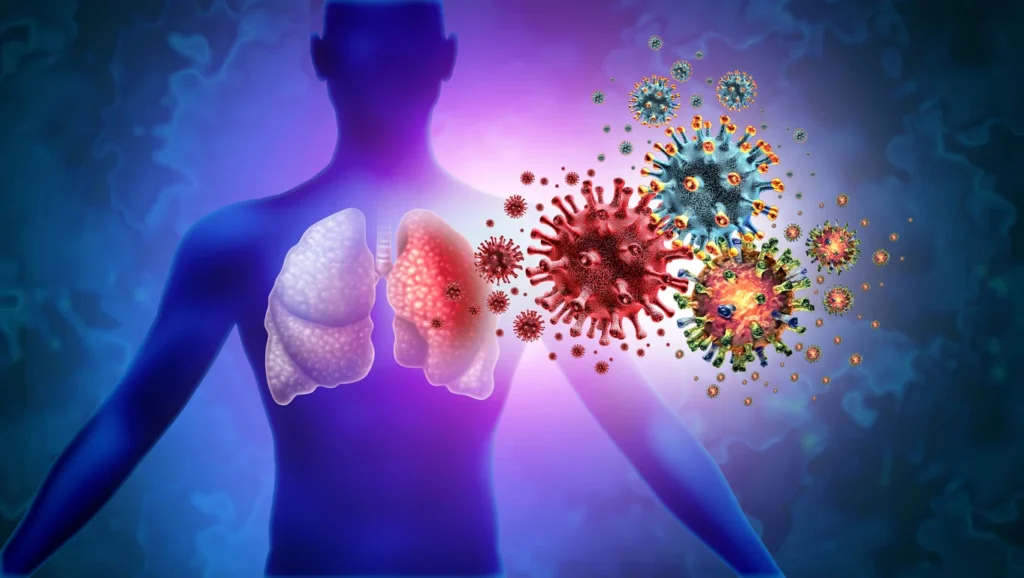
Low vitamin D levels can weaken your immune system, making you more susceptible to respiratory infections like the common cold, bronchitis, and even COVID-19.
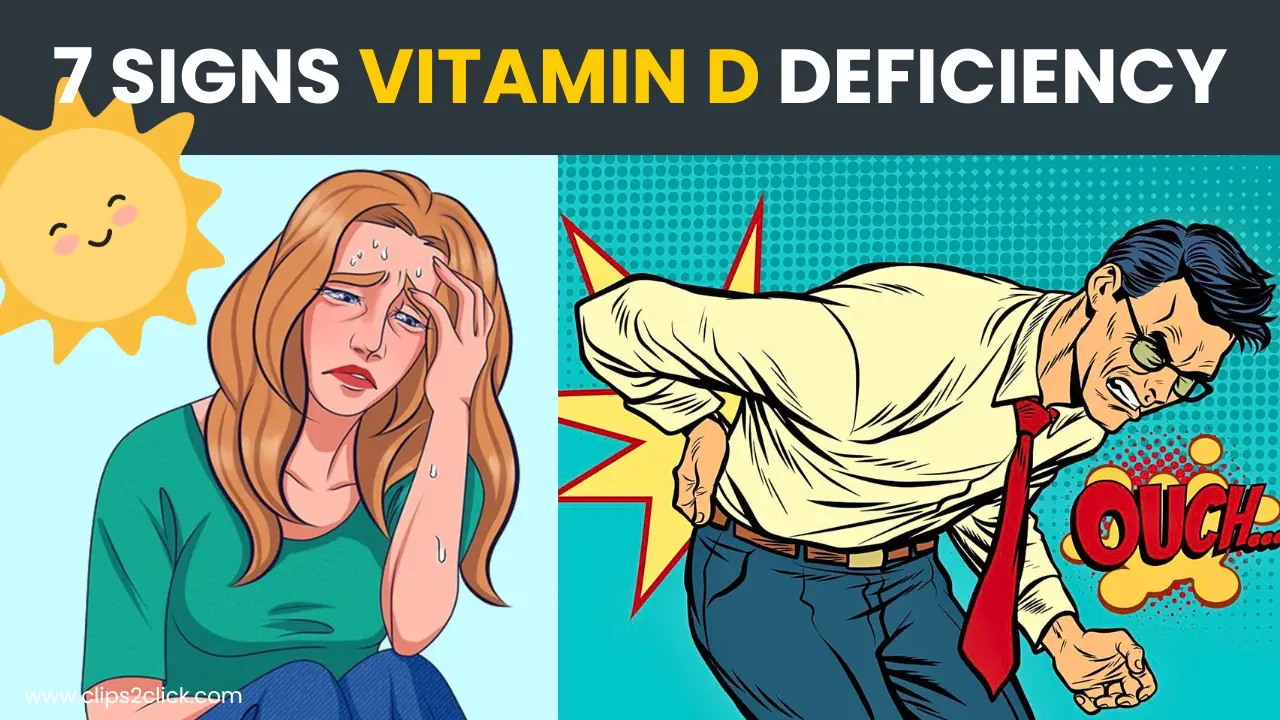
2. Persistent Fatigue and Tiredness:

Vitamin D deficiency has been linked to feelings of excessive tiredness, poor sleep quality, and a general lack of energy.
3. Bone and Back Pain:
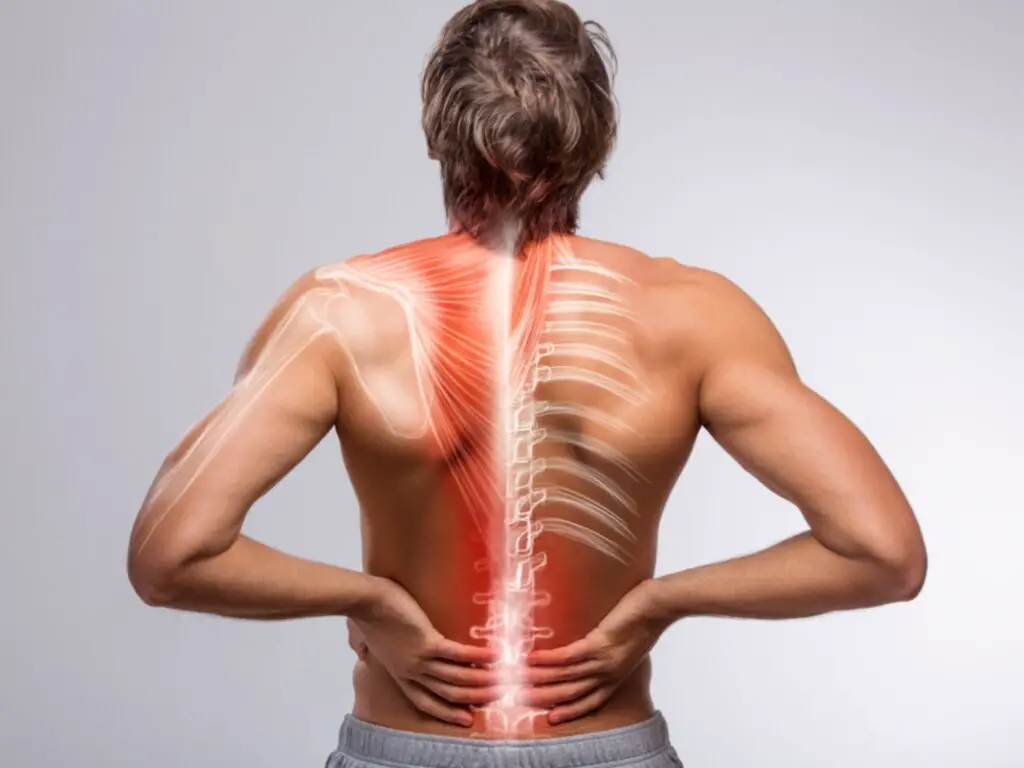
Vitamin D aids in calcium absorption, and a deficiency can lead to bone pain, lower back discomfort, and an increased risk of osteoporosis.
4. Mood Disorders:

Some studies suggest a connection between low vitamin D levels and an increased risk of anxiety and depression, particularly in older adults.
5. Impaired Wound Healing:

Vitamin D plays a role in the wound-healing process, and a deficiency can slow recovery from injuries or surgeries.
6. Hair Loss:

Severe vitamin D deficiency has been associated with alopecia areata, an autoimmune condition that causes hair loss.
7. Muscle Pain:

Vitamin D receptors are present in nerve cells that sense pain, and a deficiency may contribute to chronic muscle pain.
Risk Factors for Vitamin D Deficiency:
While anyone can develop a vitamin D deficiency, certain factors increase your risk, including;
- having darker skin tones,
- being an older adult,
- living in regions with limited sunlight exposure,
- obesity, and
- certain medical conditions that affect nutrient absorption.
Treating Vitamin D Deficiency:
If you suspect a vitamin D deficiency, consult with your healthcare provider for a blood test. Depending on the severity of the deficiency, treatment may involve:

- Dietary Changes: Incorporating vitamin D-rich foods like fatty fish, egg yolks, fortified cereals, and dairy products can help boost your levels.
- Vitamin D Supplements: Over-the-counter vitamin D supplements, such as cholecalciferol, may be recommended by your healthcare provider.
- Prescription Vitamin D: For severe deficiencies, your doctor may prescribe high-dose vitamin D supplements or consider vitamin D injections.
- Sun Exposure: Spending moderate time in the sun (with proper sun protection) can stimulate your body’s natural vitamin D production.
Maintaining Optimal Vitamin D Levels:

Addressing a vitamin D deficiency is crucial for supporting your overall health and well-being. By recognizing the telltale signs and taking proactive steps to maintain optimal vitamin D levels, you can reduce your risk of chronic diseases, boost your immune system, and improve your overall quality of life.
Remember, if you’re experiencing any of the symptoms mentioned above, don’t hesitate to consult with your healthcare provider. Early detection and appropriate treatment can go a long way in restoring your vitamin D levels and promoting better health.
References
- Spritzler, F. (2018). 8 Signs and Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency. [online] Healthline. Available at: https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/vitamin-d-deficiency-symptoms
- WebMD (2022). Vitamin D Deficiency: Symptoms, Causes, and Health Risks. [online] WebMD. Available at: https://www.webmd.com/diet/vitamin-d-deficiency.
- MedlinePlus (2019). Vitamin D Deficiency. [online] Medlineplus.gov. Available at: https://medlineplus.gov/vitaminddeficiency.html.