Vitamin K Deficiency Symptoms: Recognizing the Signs of This Dangerous Bleeding Disorder
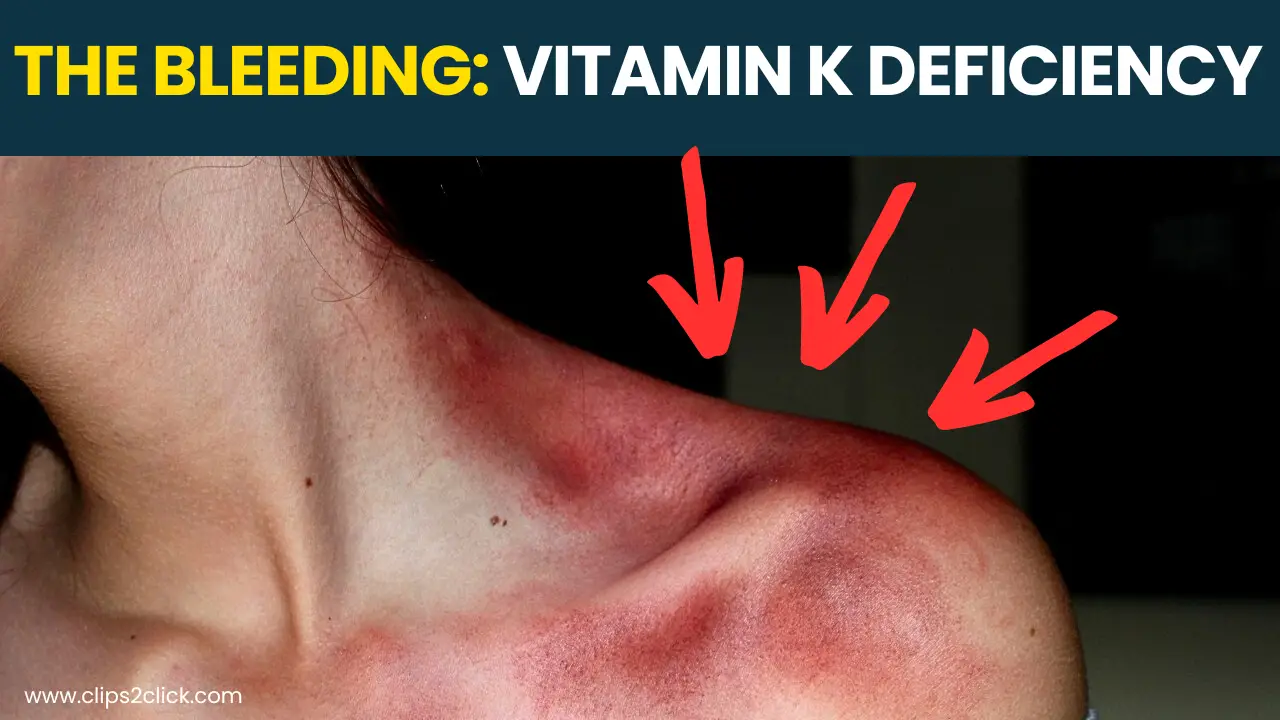
Have you noticed unusual bruising lately? Maybe a small cut won’t stop bleeding? These could actually be signs of vitamin K deficiency – a dangerous condition causing abnormal bleeding.
Vitamin K is an essential nutrient for blood clotting and bone health. Without enough, your blood struggles to clot properly, increasing your risk of excessive or uncontrolled bleeding.
While rare in adults, vitamin K deficiency can lead to scary symptoms you shouldn’t ignore.
The Main Vitamin K Deficiency Symptoms
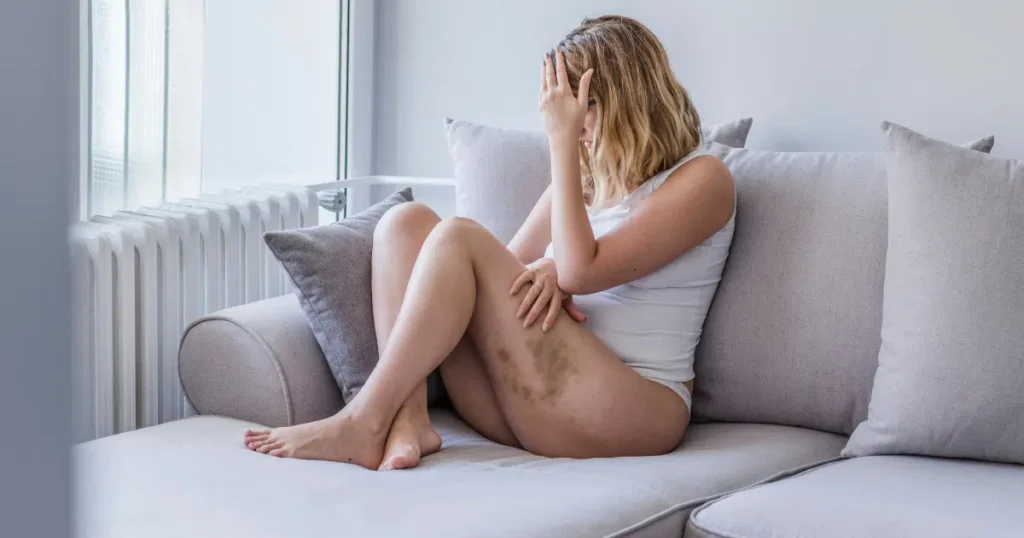
Easy bruising is one of the top vitamin K deficiency symptoms to watch for. You may notice frequent bruises appearing, even without any injury.
Bleeding that won’t stop after a minor cut or hitting your arm is another red flag. Women might experience heavy, abnormal menstrual bleeding.
As the deficiency worsens, you could start bleeding from the nose or gums. You may even cough up blood or have bloody stools, indicating internal bleeding is occurring.
For infants, vitamin K deficiency bleeding (VKDB) symptoms range from bleeding from the umbilical cord stump to sudden brain hemorrhaging – which can prove fatal if untreated.
What Causes Vitamin K Deficiency?

Most adults consume adequate vitamin K through their diet or from bacteria producing it in the gut. However, certain risk factors increase chances of deficiency.
Medical conditions impairing vitamin K absorption, like cystic fibrosis, celiac disease, gallbladder disease or intestinal disorders put you at higher risk. Having part of your intestines removed also impacts absorption.
Long-term antibiotic use may deplete vitamin K by killing the good gut bacteria that produce it. Blood thinners like warfarin can also cause deficiency by interfering with vitamin K.
Newborns face highest vitamin K deficiency risk since breastmilk is low in vitamin K. Their undeveloped liver struggles to use it efficiently too.
Diagnosis and Treatment
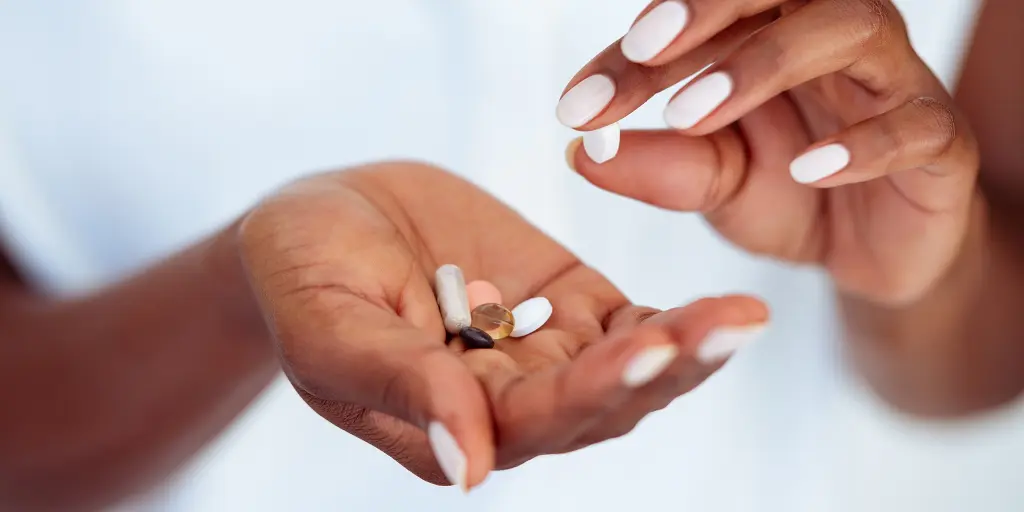

If experiencing abnormal bruising or bleeding, see your doctor immediately. Simple blood tests can check vitamin K levels and clotting ability.
Treatment focuses on quickly replenishing vitamin K stores, often through injections or high-dose oral vitamin K supplements. Severe deficiencies may require ongoing vitamin K therapy or dietary changes with vitamin K rich foods like leafy greens.
Don’t ignore warning signs like easy bruising or unexplained bleeding. Early diagnosis and treatment of vitamin K deficiency is crucial to prevent potentially life-threatening bleeding events.
While rare, adults with certain underlying conditions like malabsorptive disorders remain at higher risk. Parents should also ensure infants receive vitamin K at birth to prevent devastating VKDB bleeding in newborns.
Stay vigilant about getting adequate vitamin K through a balanced diet with foods high in vitamin K, vitamin k supplements or multivitamin. Doing so helps your blood clot normally and supports strong, healthy bones too!